Abstract
Case Report
Overlap of two unusual condition in childhood: hibernoma and central diabetes insipidus
Kübra ARSLAN*, Ayça TÖREL ERGÜR and Mehmet Ali YİNANÇ
Published: 07 March, 2022 | Volume 6 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-003
Central Diabetes Insipidus (CDI) results from the inability to secrete ADH secreted by the neurohypophysis system to control water-electrolyte metabolism. In the etiology of CDI in childhood, many congenital and acquired central nervous system (CNS) tumors (germinoma, pinealoma, craniopharyngioma, optic glioma, acute myeloid leukemia), infiltrative diseases (Langerhans cell histiocytosis, sarcoidosis), infections (meningitis, tuberculosis, encephalitis), autoimmune events, head trauma, idiopathic) can be responsible [1]. Hibernomas, which are very rare in childhood, may also rarely involve the central nervous system.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001023 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
References
- Di Lorgi N, Napoli F, Allegri AEM, Olivieri I, Bertelli E, et al. Diabetes Insipidus – diagnosis and management. Horm Res Paediatr. 2012; 77: 69–84. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22433947/
- Mermer M, Acar Tek N. Adipose tissue and its effects on energy metabolism. Süleyman Demirel University J Health Sci. 2017; 40-46.
- Van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Vanhommerig JM, Smulders NM, Drossaerts JMAFL, Kemerink GJ, et al. Cold-activated Brown adipose tissue in healty men. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360: 1500-1508. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19357405/
- Trujillo O, Cui IH, Malone M, Suurna M. An unusual presentation of a rare benign tumor in head and neck: a review of hibernomas. Laryngoscope. 2015; 125: 1656-1659. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25583551/
- Guidry CA, McGahren ED, Rodgers BM, Kane BJ. Pediatric cervicomediastinal hibernoma: A case report. J Ped Surg.2013; 48: 258-261. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23331827/
- Evers LH, Gebhard M, Lange T, Siemers F, Mailänder P. Hibernoma – Case Report and Literature Review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009; 31: 685-686. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19668076/
- Honoki K, Morita K, Kasai T, Fujii H, Kido A, et al. Hibernoma of the axillary region: a rare benign adipocytic tumor. Rare Tumors. 2010; 2: 20-21. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21139952/
- Ahmed SA, Schuller I. Pediatric Hibernoma: A Case Report. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2008; 30: 900-901.
- DeRosa DC, Lim RB, Lin-Hurtubise K, Johnson EA. Symptomatic hibernoma: a rare soft tissue tumor. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2012; 71: 342-345. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23251871/
- Fujiwara TM, Bichet DG. Molecular biology of hereditary diabetes insipidus. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005; 16: 2836–2846. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16093448/
- Patti G, Ibba A, Morana G, Napoli F, Fava D, et al. Central diabetes insipidus in children: Diagnosis and management. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020; 34: 101440. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32646670/
- Rigoli L, Aloi C, Salina A, Di Bella C, Salzano G, et al. Wolfram syndrome 1 in the Italian population: genotype–phenotype correlations. Pediatr Res. 2020; 87: 456-462. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31266054/
- Little BP, Fintelmann FJ, Mino-Kenudson M, Lanuti M, Shepard JO, et al. Intrathoracic Hibernoma. A case with multimodality imaging correlation. J Thorac Imaging. 2011; 26: W20-22. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20871421/
- Mugel T, Ghoussain MA, Guinet C. MR and CT Findings in a case of hibernoma of the thigh extending into the pelvis. Eur Radiol. 1998; 8: 476-478.
- Ghirardello S, Garre ML, Rossi A, Maghnie M. The diagnosis of children with central diabetes insipidus. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 20: 359–375. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17451074/
- Ghirardello S, Malattia C, Scagnelli P, Maghnie M. Current perspective on the pathogenesis of central diabetes insipidus. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 8: 631-645. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16128239/
Figures:
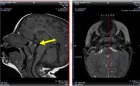
Figure 1

Figure 2
Similar Articles
-
Recurrent Cardiac Events Driven by Prothrombotic Burden in a Patient Undergoing Lipoprotein Apheresis for High Lp(a) LevelsGabriele Cioni*,Rossella Marcucci,Rosanna Abbate,Giovanna D’Alessandri. Recurrent Cardiac Events Driven by Prothrombotic Burden in a Patient Undergoing Lipoprotein Apheresis for High Lp(a) Levels. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hcem.1001001; 1: 001-005
-
Effect on Vitamin D status of Breastfeeding Infants after Vitamin D3 Supplementation during Breastfeeding Lactation: A double-blind randomized controlled trialSathit Niramitmahapanya*,Surasak Kaoiean,Varaporn Sangtawesin,Anusorn Patpanaprapan,Narisa K Bordeerat,Chaicharn Deerochanawong. Effect on Vitamin D status of Breastfeeding Infants after Vitamin D3 Supplementation during Breastfeeding Lactation: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hcem.1001002; 1: 006-014
-
Parathyroid Functions in Thalassemia Major PatientsAyfer Gözü Pirinççioğlu*,Deniz Gökalp,Murat Söker. Parathyroid Functions in Thalassemia Major Patients. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hcem.1001003; 1: 015-019
-
Diabetes and red blood cell parametersMd. Sadikuj Jaman*,Md. Sohanur Rahman,Rubaiya Rafique Swarna,Joyanto Mahato,Md. Milon Miah,Mosa. Ayshasiddeka. Diabetes and red blood cell parameters. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001004; 2: 001-009
-
Indian spices and Caffeine treatment for Obesity and Cardiovascular diseaseIan James Martins*. Indian spices and Caffeine treatment for Obesity and Cardiovascular disease. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001005; 2: 010-014
-
New pharmacological strategies in some metabolic endocrine disorder under a toxicological approachLuisetto M*,Ghulam Rasool Mashori,Cabianca luca. New pharmacological strategies in some metabolic endocrine disorder under a toxicological approach. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001006; 2: 015-021
-
Exercise preserves pancreatic β-cell mass and function in obese OLETF ratsJiawei Zhao,Zhihong Yang,Min He,Qinghua Wang,Renming Hu*. Exercise preserves pancreatic β-cell mass and function in obese OLETF rats. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001007; 2: 022-029
-
A Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with an Unusual FlushNathania Sutandi*,Steven White. A Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor with an Unusual Flush. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001008; 2: 030-032
-
Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Hydroxychloroquine and Teneligliptin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients who are Inadequately Controlled with Glimepiride, Metformin and Insulin therapy: A Randomized Controlled Trial with Parallel Group DesignPrakash Ranjan,Sajjad Ahsan*,Rabi Bhushan,Bipin Kumar,Tushar,Anup Kumar Gupta,Anand Kumar Verma,Mukesh Jain. Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Hydroxychloroquine and Teneligliptin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients who are Inadequately Controlled with Glimepiride, Metformin and Insulin therapy: A Randomized Controlled Trial with Parallel Group Design. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001009; 2: 033-040
-
Endocrine abnormalities in two siblings with Rothmund Thomson SyndromeNagehan Aslan*,Ozgur Pirgon. Endocrine abnormalities in two siblings with Rothmund Thomson Syndrome. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001010; 2: 041-045
Recently Viewed
-
Phenotypic differences in Obese Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) - A Mini ReviewMichelle Nanni*, Vivian Hu, Swagata Patnaik, Alejandro Folch Sandoval, Johanna Contreras. Phenotypic differences in Obese Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) - A Mini Review. New Insights Obes Gene Beyond. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.niogb.1001020; 8: 001-005
-
Stone on the Mesh: Intravesical Erosion after Laparoscopic Promontofixation-A Hidden Cost of DurabilityAyoub Mamad*,Mohammed Amine Bibat,Mohammed Amine Elafari,Midaoui Moncef,Amine Slaoui,Tarik Karmouni,Abdelatif Koutani,Khalid Elkhader. Stone on the Mesh: Intravesical Erosion after Laparoscopic Promontofixation-A Hidden Cost of Durability. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001040; 10: 006-009
-
Febrile Lumbar Pain Revealing a Massive Collection: Complicated Psoas Abscess Managed SurgicallyMohammed Amine Elafari*,Mamad Ayoub,Mohammed Amine Bibat,Rhayour Anas,Maachi Youssef,Amine Slaoui,Tarik Karmouni,Abdelatif Koutani,Khalid Elkhader. Febrile Lumbar Pain Revealing a Massive Collection: Complicated Psoas Abscess Managed Surgically. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001041; 10: 010-012
-
Feasibility study on the evaluation of the effect of narrow-band CE-Chirp ASSR in the hearing field after hearing aid in hearing-impaired childrenWang Yonghua*,Xing Shuoyao. Feasibility study on the evaluation of the effect of narrow-band CE-Chirp ASSR in the hearing field after hearing aid in hearing-impaired children. Adv Treat ENT Disord. 2019: doi: 10.29328/journal.ated.1001007; 3: 007-011
-
Impact of Community Oriented Ear Care (COEC) on national programme for control of deafness in India: A critical lookSanjeev Davey*,Anuradha Davey,Rajesh Jain. Impact of Community Oriented Ear Care (COEC) on national programme for control of deafness in India: A critical look. Adv Treat ENT Disord. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.ated.1001009; 4: 001-002
Most Viewed
-
Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trialSathit Niramitmahapanya*,Preeyapat Chattieng,Tiersidh Nasomphan,Korbtham Sathirakul. Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001026; 7: 00-007
-
Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and RehabilitationCristina Popescu, Mircea-Sebastian Șerbănescu, Gigi Calin*, Magdalena Rodica Trăistaru. Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and Rehabilitation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001030; 8: 004-012
-
Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging PresentationKarthik Baburaj*, Priya Thottiyil Nair, Abeed Hussain, Vimal MV. Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging Presentation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001029; 8: 001-003
-
Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-goDaniel Gandia,Cecilia Suárez*. Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-go. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001033; 7: 001-002
-
The benefits of biochemical bone markersSek Aksaranugraha*. The benefits of biochemical bone markers. Int J Bone Marrow Res. 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001013; 3: 027-031

If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."