Abstract
Letter to Editor
Myxedema coma in COVID-19
Yuichi Takashi* and Daiji Kawanami*
Published: 31 July, 2021 | Volume 5 - Issue 1 | Pages: 029-030
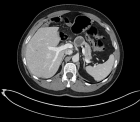
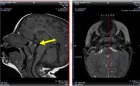
SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with thyroid disorders. It has been reported that myxedema coma (MC) can be complicated with COVID-19. COVID-19-related thyroid disorders consist of a broad spectrum of thyroid dysfunction, from thyrotoxicosis to decompensated hypothyroidism. It is possible that both primary and central thyroid disorders are induced by COVID-19 due to systemic inflammatory and immune responses. We experienced two cases in which patients with COVID-19 developed MC with central hypothyroidism. It is likely that MC affected the severity of COVID-19. It is necessary to consider the existence of MC during SARS-CoV-2 infection. We propose the potential mechanisms.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001021 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Myxedema; Coma; SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19; Cytokine release syndrome
References
- Sinha P, Calfee CS, Cherian S, Brealey D, Cutler S, et al. Prevalence of phenotypes of acute respiratory distress syndrome in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a prospective observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020; 8: 1209-1218. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32861275/
- Ono Y, Ono S, Yasunaga H, Matsui H, Fushimi K, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of myxedema coma: Analysis of a national inpatient database in Japan. J Epidemiol. 2017; 27: 117-22. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28142035/
- Mathew V, Misgar RA, Ghosh S, Mukhopadhyay P, Roychowdhury P, et al. Myxedema coma: a new look into an old crisis. J Thyroid Res. 2011; 2011: 493462. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21941682/
- Dixit NM, Truong KP, Rabadia SV, Li D, Srivastava PK, et al. Sudden Cardiac Arrest in a Patient With Myxedema Coma and COVID-19. J Endocr Soc. 2020; 4: bvaa130. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32984743/
- Caron P. Thyroid disorders and SARS-CoV-2 infection: From pathophysiological mechanism to patient management. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2020; 81: 507-510. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32950466/
- Jara EL, Munoz-Durango N, Llanos C, Fardella C, Gonzalez PA, et al. Modulating the function of the immune system by thyroid hormones and thyrotropin. Immunol Lett. 2017; 184: 76-83. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28216261/
- Wei L, Sun S, Xu CH, Zhang J, Xu Y, et al. Pathology of the thyroid in severe acute respiratory syndrome. Hum Pathol. 2007; 38: 95-102. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16996569/
- Pal R. COVID-19, hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis and clinical implications. Endocrine. 2020; 68: 251-252. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32346813/
Similar Articles
-
Management of gestational diabetes during ‘COVID19 time’Nicolina Di Biase*. Management of gestational diabetes during ‘COVID19 time’. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001015; 4: 020-022
-
COVID-19 associated hyperthyroidism due to destructive thyrotoxicosis in a young female patientZeilberger MS*,Hasmann SE*,Auer MK,Schmidmaier R. COVID-19 associated hyperthyroidism due to destructive thyrotoxicosis in a young female patient. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001016; 4: 023-025
-
Myxedema coma in COVID-19Yuichi Takashi*,Daiji Kawanami*. Myxedema coma in COVID-19. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001021; 5: 029-030
-
Myxedema Coma and Acute Respiratory Failure in a Young Child: A Case ReportRinah Elaisse R Dolores, Marion O Sanchez*. Myxedema Coma and Acute Respiratory Failure in a Young Child: A Case Report. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001027; 7: 008-013
Recently Viewed
-
Looking Beyond Common Causes of Renal Dysfunction: Renal GVHD and Thrombotic Microangiopathy after Allogeneic TransplantTaner Tan*,Ahmet Umur Topcu,Erdem Cig,Dilek Ertoy Baydar,Sinem Civriz Bozdag. Looking Beyond Common Causes of Renal Dysfunction: Renal GVHD and Thrombotic Microangiopathy after Allogeneic Transplant. Insights Clin Cell Immunol. 2026: doi: ; 10: 001-003
-
Chlorhexidine and oral cancer: A short reviewShrivardhan R Kalghatgi*,Mahesh R Khairnar,Tanushri Dalvi. Chlorhexidine and oral cancer: A short review. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001012; 4: 001-002
-
A retrospective study for Colorectal Cancer in Vlore, Albania-suggestions for further implicationsFatjona Kamberi*,Jerina Jaho. A retrospective study for Colorectal Cancer in Vlore, Albania-suggestions for further implications. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001013; 4: 003-006
-
Vegetables associated with reduced risk of cancerRobert Skopec*. Vegetables associated with reduced risk of cancer. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001014; 4: 007-014
-
Palliative care approach to oncological patient – Main pointsOnur Öztürk*,Muhammed Emin Göktepe,Mustafa Ünal. Palliative care approach to oncological patient – Main points. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001015; 4: 015-016
Most Viewed
-
Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trialSathit Niramitmahapanya*,Preeyapat Chattieng,Tiersidh Nasomphan,Korbtham Sathirakul. Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001026; 7: 00-007
-
Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and RehabilitationCristina Popescu, Mircea-Sebastian Șerbănescu, Gigi Calin*, Magdalena Rodica Trăistaru. Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and Rehabilitation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001030; 8: 004-012
-
Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging PresentationKarthik Baburaj*, Priya Thottiyil Nair, Abeed Hussain, Vimal MV. Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging Presentation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001029; 8: 001-003
-
Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-goDaniel Gandia,Cecilia Suárez*. Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-go. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001033; 7: 001-002
-
The benefits of biochemical bone markersSek Aksaranugraha*. The benefits of biochemical bone markers. Int J Bone Marrow Res. 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001013; 3: 027-031

If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."